|
We
first presented our findings: "Le Bioclimatique en Milieu Urbain Dense"
(Passive solar design in a dense urban setting), at a 1993 seminar
organised by the International Solar Energy Society, and ADEME, in
Sophia Antipolis, France.
They
were illustrated by a proposal for the Seine-Rive-Gauche neighborhood
in Paris, a railroad fallow land area to be developped.
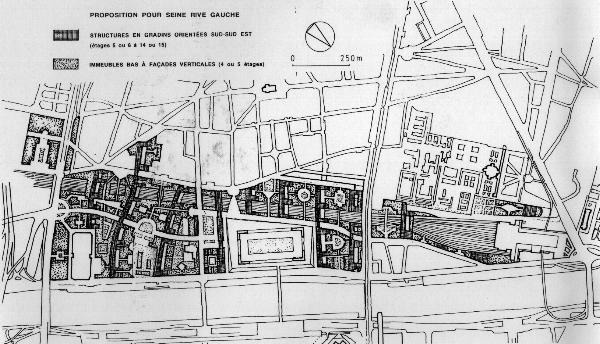
Passive solar design in a dense urban setting
for Seine Rive Gauche in Paris (JL Msika)
In
place of a succession of mono-functional buildings, all of the same
height, and therefore denying each other access to winter sun, it is a
fluid, organic and evolutionary configuration, designed to receive
solar light and heat naturally.
By
superimposing the diverse and simultaneous urban functions
characterizing a living whole, and combining them organically, one can
optimize their relation to public space and sunshine, and create a
diversified urban environment on a human scale, with an effective
limitation of air pollution.
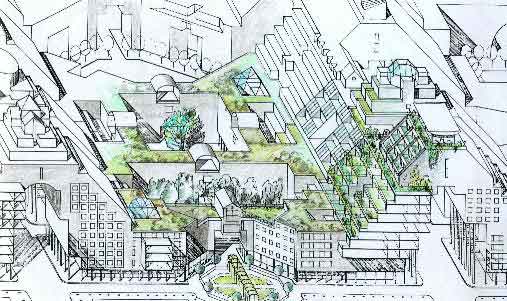
Passive
solar in a dense mixed-use setting will also definitely be a green
city, with urban parks and gardens,
tree lined avenues and streets, and stepped housing with conservatories
and private gardens on all floors.
"Seine-Rive-Gauche"
district, 130 hectares of railroad fallow land,
which
were to be developed in Paris, in 1993 (JL Msika)
|

